1,3-Dioxane
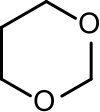
1,3-Dioxane or m-dioxane is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C4H8O2.[1] It is a saturated six-membered heterocycle with two oxygen atoms in place of carbon atoms at the 1- and 3- positions. The corresponding five-membered rings are known as 1,3-dioxolanes.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Formaldehyde trimethylene acetal | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
Beilstein Reference |
102532 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.278 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1165 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C4H8O2 |
| Molar mass | 88.106 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | −42 °C (−44 °F; 231 K) |
| Boiling point | 103 °C (217 °F; 376 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H225, H302, H312, H315, H332 |
GHS precautionary statements |
P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+313, P362, P363, P370+378, P403+235 |
| Flash point | 2 °C (36 °F; 275 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Like 1,3-dioxolanes, 1,3-dioxanes are acetals which can be used as protecting groups for carbonyl compounds. They are prepared from the reaction between carbonyl compounds (formaldehyde for the parent 1,3-dioxane) and 1,3-propanediol in the presence of Brönsted or Lewis acid catalysts.[2]
See also
- 1,2-Dioxane
- 1,4-Dioxane
- Dithiane
References
- Sigma-Aldrich Co., 1,3-Dioxane 97%.
- Greene, Theodora W.; Wuts, Peter G. M. (1999). "1,3-Dioxanes, 1,3-Dioxolanes". Greene's Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis (3rd ed.). Wiley-Interscience. pp. 308–322, 724–727. ISBN 9780471160199. Archived from the original on December 7, 2016. Retrieved June 12, 2020.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.