Allylamine
Allylamine is an organic compound with the formula C3H5NH2. This colorless liquid is the simplest stable unsaturated amine.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Prop-2-en-1-amine[1] | |
| Other names
2-Propen-1-amine 2-Propenamine Allyl amine 3-Amino-prop-1-ene 3-Aminopropene 3-Aminopropylene Monoallylamine | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.150 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2334 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C3H7N |
| Molar mass | 57.096 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.7630 g/cm3, liquid |
| Melting point | −88 °C (−126 °F; 185 K) |
| Boiling point | 55 to 58 °C (131 to 136 °F; 328 to 331 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.49 (conjugate acid; H2O)[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Lachrymatory |
| GHS pictograms |      |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H225, H301, H310, H315, H319, H330, H335, H371, H373, H401, H411 |
GHS precautionary statements |
P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P262, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+310, P302+350, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P309+311, P310, P312, P314 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
3
4 |
| Flash point | −28 °C (−18 °F; 245 K) |
Autoignition temperature |
374 °C (705 °F; 647 K) |
| Explosive limits | 2-22% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
106 mg/kg |
| Related compounds | |
Related amine |
Propylamine |
Related compounds |
Allyl alcohol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Production and reactions
All three allylamines, mono-, di-, and triallylamine, are produced by the treating allyl chloride with ammonia followed by distillation.[3] Or by the reaction of allyl chloride with Hexamine.[4] Pure samples can be prepared by hydrolysis of allyl isothiocyanate.[5] It behaves as a typical amine.[6]
Polymerization can be used to prepare the homopolymer (polyallylamine) or copolymers. The polymers are promising membranes for use in reverse osmosis.[3]
Other allylamines
Functionalized allylamines have extensive pharmaceutical applications. Pharmaceutically important allylamines include flunarizine and naftifine. Flunarizine aids in the relief of migraines while naftifine acts to fight common fungus causing infections such as athlete's foot, jock itch, and ringworm.[7]
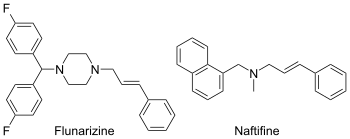
Safety
Allylamine, like other allyl derivatives is a lachrymator and skin irritant. Its oral LD50 is 106 mg/kg for rats.
References
- Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 681. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- Hall, H. K. (1957). "Correlation of the Base Strengths of Amines". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 79 (20): 5441–5444. doi:10.1021/ja01577a030.
- Ludger Krähling; Jürgen Krey; Gerald Jakobson; Johann Grolig; Leopold Miksche (2002). "Allyl Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_425.
- "Synthesis of allylamine in ethanol". ResearchGate. Retrieved 2020-06-30.
- M. T. Leffler (1943). "Allylamine". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, 2, p. 24
- Henk de Koning, W. Nico Speckamp "Allylamine" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/047084289X.ra043 Article Online Posting Date: April 15, 2001
- Beck, John F.; Samblanet, Danielle C.; Schmidt, Joseph A. R. (1 January 2013). "Palladium catalyzed intermolecular hydroamination of 1-substituted allenes: an atom-economical method for the synthesis of N-allylamines". RSC Advances. 3 (43): 20708. doi:10.1039/c3ra43870h.
External links
- Allylamine from PubChem at National Center for Biotechnology Information