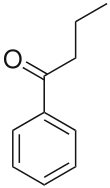
Butyrophenone
Butyrophenone is a chemical compound; some of its derivatives (called commonly butyrophenones) are used to treat various psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, as well as acting as antiemetics.[1]
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-phenylbutan-1-one | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
|||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.091 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula |
C10H12O | ||
| Molar mass | 148.20 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | clear liquid | ||
| Melting point | 12 °C (54 °F; 285 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 229 °C (444 °F; 502 K) | ||
Solubility in water |
poor | ||
| log P | 2.77 | ||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.520 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
1
1
1 | ||
| Flash point | 99 °C (210 °F; 372 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Examples of butyrophenone-derived pharmaceuticals include:
- Haloperidol, the most widely used classical antipsychotic drug in this class[1]
- Benperidol, the most potent commonly used antipsychotic (200 times more potent than chlorpromazine)[1][2]
- Droperidol, Antiemetic for postoperative nausea and vomiting
References
- Keith Parker; Laurence Brunton Goodman; Louis Sanford; Lazo, John S.; Gilman, Alfred (2006). Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (11th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0071422803.
- Grogan, Charles H.; Rice, Leonard M. (1967). "Ω-Azabicyclic Butyrophenones". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 10 (4): 621. doi:10.1021/jm00316a022. PMID 6037051.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.