Hexanitroethane
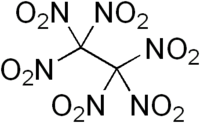
Hexanitroethane (HNE) is an organic compound with chemical formula C2N6O12 or (O2N)3C-C(NO2)3. It is a solid matter with a melting point of 135 °C.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,1,1,2,2,2-Hexanitroethane | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.857 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C2N6O12 |
| Molar mass | 300.0544 |
| Melting point | 135 °C (275 °F; 408 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Nitroethane Tetranitromethane Trinitromethane Hexanitrobenzene Octanitrocubane |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Hexanitroethane is used in some pyrotechnic compositions as a nitrogen-rich oxidizer, e.g. in some decoy flare compositions and some propellants. Like hexanitrobenzene, HNE is investigated as a gas source for explosively pumped gas dynamic laser.
A composition of HNE as oxidizer with boron as fuel is being investigated as a new explosive.[1]
References
- Compatibility Testing of Hexanitroethane with Boron Archived September 30, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.