Potassium dideuterium phosphate
Deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KD2PO4) or DKDP single crystals are widely used in non-linear optics as the second, third and fourth harmonic generators for Nd:YAG and Nd:YLF lasers. They are also found in electro-optical applications as Q-switches for Nd:YAG, Nd:YLF, Alexandrite and Ti-sapphire lasers, as well as for Pockels cells.[1]
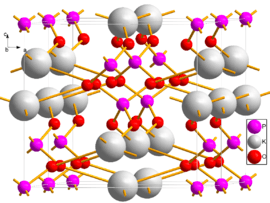 Two unit cells of DKDP viewed close to the b axis | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
KD 2PO 4 |
| Molar mass | 138.10 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
DKDP is closely related to monopotassium phosphate or KDP or KH2PO4. Replacement of hydrogen by deuterium in DKDP lowers the frequency of O-H vibrations and their overtones (high-order harmonics). Absorption of light by those overtones is detrimental for the infrared lasers, which DKDP and KDP crystals are used for. Consequently, despite higher cost, DKDP is more popular than KDP.
DKDP crystals are grown by a water-solution method at usual level of deuteration >98%.
See also
- Beta barium borate (BBO) – another popular non-linear crystal
- Lithium triborate (LBO) – another popular non-linear crystal
- Monopotassium phosphate (KDP) – another popular non-linear crystal
- Non-linear optics
- Potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) – another popular non-linear crystal
- Second harmonic generation (SHG)
- Third harmonic generation (THG)
- Two-photon absorption (TPA)
- Organic nonlinear optical materials