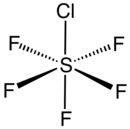
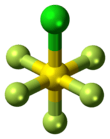
Sulfur chloride pentafluoride
Sulfur chloride pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula SF
5Cl. It exists as a colorless gas at room temperature and is highly toxic, like most inorganic compounds containing the pentafluorosulfide (SF5) functional group.[1] The compound adopts an octahedral geometry with C
4v symmetry. Sulfur chloride pentafluoride is the only commercially available reagent for adding the SF
5 group to organic compounds.[2][3]
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Other names
Pentafluorochlorosulfanyl | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
|||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.014 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula |
SClF 5 | ||
| Molar mass | 162.510 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Density | 6.642 g dm−3 | ||
| Melting point | −64 °C (−83 °F; 209 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −19 °C (−2 °F; 254 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Toxic | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Reactivity
In contrast to the high reactivity and toxicity of SF
5Cl, sulfur hexafluoride (SF
6), is inert and nontoxic despite having a closely related chemical formula. This difference highlights the lability of the S-Cl bond in this molecule.
Under free-radical conditions, SF
5Cl adds across double bonds. The following reaction involves the reaction of propene:
- CH
3CHCH
2 + SF
5Cl → CH3CH(Cl)CH2SF5
The addition reaction is catalyzed by Et
3B at around -30 °C. SF
5Br is used similarly.[2]
SF
5Cl is also a precursor to O(SF5)2 and F2NSF5 (from tetrafluorohydrazine).
Synthesis
Sulfur chloropentafluoride can be synthesized by several routes, starting from two lower sulfur fluorides, sulfur tetrafluoride and disulfur decafluoride:[1]
- SF
4 + Cl
2 + CsF → SF
5Cl + CsCl - ClF + SF
4 → SF
5Cl - S
2F
10 + Cl
2 → 2 SF
5Cl
The corresponding SF
5Br is prepared similarly from in-situ generated bromine monofluoride.[4]
References
- Nyman, F., Roberts, H. L., Seaton, T. "Sulfur Chloride Pentafluoride" Inorganic Syntheses, 1966, Volume 8, p. 160. doi:10.1002/9780470132395.ch42
- Dolbier, William R.; et al. (2006). "A convenient and efficient method for incorporation of pentafluorosulfanyl (SF5) substituents into aliphatic compounds". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 127 (10): 1302–10. doi:10.1016/j.jfluchem.2006.05.003.
- Savoie, Paul R.; Welch, John T. (2015). "Preparation and Utility of Organic Pentafluorosulfanyl-Containing Compounds". Chemical Reviews. 115 (2): 1130–1190. doi:10.1021/cr500336u. PMID 25341449.
- Winter, Rolf; Terjeson, Robin J.; Gard, Gary L. (1998). "An Improved and Facile Preparation of SF5Br". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 89: 105–106. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(98)00094-3.