1,2-Diaminopropane
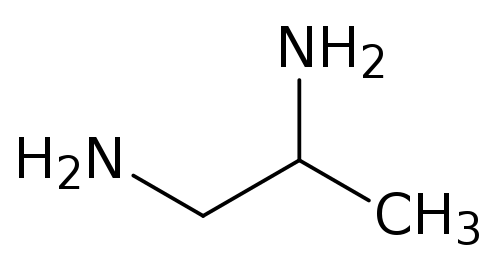
1,2-Diaminopropane (propane-1,2-diamine) is organic compound with the formula CH3CH(NH2)CH2NH2. A colorless liquid, it is the simplest chiral diamine. It is used as a bidentate ligand in coordination chemistry.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2-Propanediamine | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Propane-1,2-diamine | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
Beilstein Reference |
605274 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.051 |
| EC Number |
|
Gmelin Reference |
25709 |
| MeSH | 1,2-diaminopropane |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2258 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C3H10N2 |
| Molar mass | 74.127 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | Fishy, ammoniacal |
| Density | 870 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point | −37.1 °C; −34.9 °F; 236.0 K |
| Boiling point | 119.6 °C; 247.2 °F; 392.7 K |
| Vapor pressure | 1.9 Pa (at 20 °C) |
Magnetic susceptibility (χ) |
-58.1·10−6 cm3/mol |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.446 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
205.64 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std molar entropy (S |
247.27 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−98.2–−97.4 kJ mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−2.5122–−2.5116 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H226, H302, H312, H314 |
GHS precautionary statements |
P280, P305+351+338, P310 |
| Flash point | 34 °C (93 °F; 307 K) |
Autoignition temperature |
360 °C (680 °F; 633 K) |
| Explosive limits | 1.9–11.1% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
|
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanamines |
|
Related compounds |
2-Methyl-2-nitrosopropane |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Preparation
Industrially, this compound is synthesized by the ammonolysis of 1,2-dichloropropane:[1]
- CH3CHClCH2Cl + 4 NH3 → CH3CH(NH2)CH2NH2 + 2 NH4Cl
This preparation allows for the use of waste chloro-organic compounds to form useful amines using inexpensive and readily available ammonia.[1]
The racemic mixture of this chiral compound may be separated into enantiomers by conversion into the diastereomeric tartaric acid ammonium salt. After purification of the diastereomer, the diamine can be regenerated by treatment of the ammonium salt with sodium hydroxide.[2] Alternate reagents for chiral resolution include N-p-toluenesulfonylaspartic acid, N-benzenesulfonylaspartic acid, or N-benzoylglutamic acid.[3]
Uses
References
- Bartkowiak, M.; Lewandowski, G.; Milchert, E.; Pelech, R. (2006). "Optimization of 1,2-Diaminopropane Preparation by the Ammonolysis of Waste 1,2-Dichloropropane". Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 45 (16): 5681–5687. doi:10.1021/ie051134u.
- Romanowski, G.; Wera, M. (2010). "Mononuclear and dinuclear chiral vanadium(V) complexes with tridentate Schiff bases derived from R(−)-1,2-diaminopropane: Synthesis, structure, characterization and catalytic properties". Polyhedron. 29 (13): 2747–2754. doi:10.1016/j.poly.2010.06.030.
- JP application 04-018057, Sakie, N. & Haruyo, S., "Production of Optically Active 1,2-propanediamine"
- Dabelstein, W.; Reglitzky A.; Schutze A.; Reders, K. "Automotive Fuels". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_719.pub2.