Allylpalladium chloride dimer
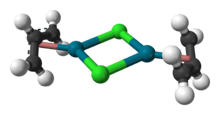
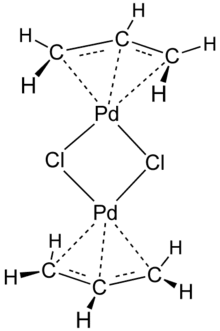
Allylpalladium(II) chloride dimer (APC) is a chemical compound with the formula [(η3-C3H5)PdCl]2. This yellow air-stable compound is an important catalyst used in organic synthesis.[1] It is one of the most widely used transition metal allyl complexes.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Allylpalladium(II) chloride dimer | |
| Other names
Allylpalladium chloride dimer bis(allyl)di-μ-chloro-dipalladium(II) APC | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.423 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C6H10Cl2Pd2 |
| Molar mass | 365.85 g/mol |
| Appearance | Pale yellow, crystalline solid |
| Density | Solid |
| Melting point | decomp at 155-156 °C |
Solubility in water |
Insoluble |
| Solubility in other solvents | Chloroform benzene acetone methanol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | http://www.colonialmetals.com/pdf/5048.pdf |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
GHS hazard statements |
H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335 |
GHS precautionary statements |
P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
(η3-allyl)(η5 – cyclopentadienyl)palladium(II) di-μ-chlorobis(crotyl)dipalladium |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Synthesis and reactions
The compound is prepared by purging carbon monoxide through a methanolic aqueous solution of sodium tetrachloropalladate (prepared from palladium(II) chloride and sodium chloride), and allyl chloride.[1]
- 2 Na2PdCl4 + 2 CH2=CHCH2Cl + 2 CO + 2 H2O → [(η3-C3H5)PdCl]2 + 4 NaCl + 2 CO2 + 4 HCl
APC reacts with sources of cyclopentadienyl anion to give the corresponding 18e complex cyclopentadienyl allyl palladium:
- [(η3-C3H5)PdCl]2 + 2 NaC5H5 → 2 [(η5-C5H5)Pd(η3-C3H5)] + 2 NaCl
The dimer reacts with a variety of Lewis bases (:B) to form adducts (η3-C3H5)PdCl:B. Its reaction with pyridine and the corresponding enthalpy are:
- 1/2[(η3-C3H5)PdCl]2 + :NC5H5 → (η3-C3H5)PdCl:NC5H5 ΔH= -30.1 kJ mol−1
This enthalpy corresponds to the enthalpy change for a reaction forming one mole of the product, (η3-C3H5)PdCl:NC5H5, from the acid dimer. The dissociation energy for the Pd dimer, which is an energy contribution prior to reaction with the donor,
- [(η3-C3H5)PdCl]2 →2 (η3-C3H5)PdCl
has been determined by the ECW model to be 28 kJ mol−1
References
- Tatsuno, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Otsuka, S. "(η3-allyl)palladium(II) Complexes" Inorganic Syntheses, 1990, volume 28, pages 342-345. ISBN 0-471-52619-3