Aluminium antimonide
Aluminium antimonide (AlSb) is a semiconductor of the group III-V family containing aluminium and antimony. The lattice constant is 0.61 nm. The indirect bandgap is approximately 1.6 eV at 300 K, whereas the direct band gap is 2.22 eV.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.410 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
AlSb |
| Molar mass | 148.742 g/mol |
| Appearance | black crystals |
| Density | 4.26 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,060 °C (1,940 °F; 1,330 K) |
| Boiling point | 2,467 °C (4,473 °F; 2,740 K) |
Solubility in water |
insoluble |
| Band gap | 1.58 eV |
Refractive index (nD) |
3.3 |
| Structure | |
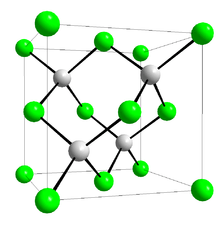
Crystal structure |
Zinc blende |
Space group |
T2d-F-43m |
Coordination geometry |
Tetrahedral |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar entropy (S |
65 J/mol K |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-50.4 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | MSDS |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
3
0
1 |
Autoignition temperature |
317 °C (603 °F; 590 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Its electron mobility is 200 cm²·V−1·s−1 and hole mobility 400 cm²·V−1·s−1 at 300 K. Its refractive index is 3.3 at a wavelength of 2 μm, and its dielectric constant is 10.9 at microwave frequencies.[1]
AlSb can be reacted with other III-V materials to produce ternary materials including AlInSb, AlGaSb and AlAsSb.
Aluminum antimonide is rather flammable because of the reducing tendency of the antimonide (Sb3−) ion. It burns to produce aluminum oxide and antimony trioxide.
References
- K Seeger and E Schonherr "Microwave dielectric constant of aluminium antimonide" Semicond. Sci. Technol. 6 (1991) 301 doi:10.1088/0268-1242/6/4/013