delta-Carotene
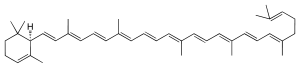
δ-Carotene or ε,ψ-carotene is a form of carotene with an ε-ring at one end, and the other uncyclized, labelled ψ (psi). It is an intermediate synthesis product in some photosynthetic plants between lycopene and α-carotene (β,ε-carotene) or ε-carotene (ε,ε-carotene).[1] δ-Carotene is fat soluble. Delta-carotene contains an alpha-ionone instead of a beta-ionone ring;[2] this conversion is carried out by the gene Del which shifts the position of the double bond in the ring structure. The formation delta-carotene under the presence of the Del gene is sensitive to high temperatures.[3]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
ε,ψ-Carotene | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C40H56 |
| Molar mass | 536.873 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Cunningham FX, Gantt E (February 2001). "One ring or two? Determination of ring number in carotenoids by lycopene epsilon-cyclases". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 98 (5): 2905–10. doi:10.1073/pnas.051618398. PMC 30238. PMID 11226339.
- Tomes ML (August 1969). "Delta-carotene in the tomato". Genetics. 62 (4): 769–80. PMC 1212314. PMID 17248458.
- Tomes ML (June 1967). "The competitive effect of the Beta- and delta-carotene genes on alpha- or Beta-ionone ring formation in the tomato". Genetics. 56 (2): 227–32. PMC 1211498. PMID 17248383.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.