Deoxyadenosine monophosphate
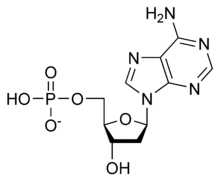
Deoxyadenosine monophosphate (dAMP), also known as deoxyadenylic acid or deoxyadenylate in its conjugate acid and conjugate base forms, respectively, is a derivative of the common nucleic acid AMP, or adenosine monophosphate, in which the -OH (hydroxyl) group on the 2' carbon on the nucleotide's pentose has been reduced to just a hydrogen atom (hence the "deoxy-" part of the name). Deoxyadenosine monophosphate is abbreviated dAMP. It is a monomer used in DNA.
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.459 |
IUPHAR/BPS |
|
| MeSH | Deoxyadenosine+monophosphate |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C10H14N5O6P |
| Molar mass | 331.222 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
- Nucleic acid
- DNA metabolism
- Cofactor
- Guanosine
- Cyclic AMP (cAMP)
- ATP
Sources
- Deoxyadenosine monophosphate at HMDB