Iodine pentafluoride
Iodine pentafluoride is an interhalogen compound with chemical formula IF5. It is one of the fluorides of iodine. It is a colorless liquid, although impure samples appear yellow. It is used as a fluorination reagent and even a solvent in specialized syntheses.[3]
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Iodine(V) fluoride | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Pentafluoro-λ5-iodane | |||
| Other names
Iodic fluoride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
|||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.108 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula |
IF5 | ||
| Molar mass | 221.89 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 3.250 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 9.43 °C (48.97 °F; 282.58 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 97.85 °C (208.13 °F; 371.00 K) | ||
Solubility in water |
Reacts | ||
Magnetic susceptibility (χ) |
−58.1·10−6 cm3/mol | ||
| Viscosity | 2.111 mPa·s | ||
| Structure | |||
Crystal structure |
monoclinic point group C2/c | ||
Coordination geometry |
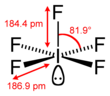
square pyramidal | ||
Molecular shape |
square pyramidal[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Toxic, oxidiser, corrosive. Releases HF upon contact with water. | ||
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS | ||
| GHS pictograms |     | ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
GHS hazard statements |
H271, H330, H311, H301, H314, H371, H410[2] | ||
GHS precautionary statements |
P202, P232, P304, P310[2] | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
0
3
2 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions |
Iodine pentoxide | ||
Other cations |
Bromine pentafluoride | ||
Related compounds |
Iodine monofluoride Iodine trifluoride Iodine heptafluoride | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Preparation
It was first synthesized by Henri Moissan in 1891 by burning solid iodine in fluorine gas.[4] This exothermic reaction is still used to produce iodine pentafluoride, although the reaction conditions have been improved.[5]
- I2 + 5 F2 → 2 IF5
Reactions
IF5 reacts vigorously with water forming hydrofluoric acid and iodic acid:
- IF5 + 3H2O → HIO3 + 5HF
Upon treatment with fluorine, it converts to iodine heptafluoride:[6]
- IF5 + F2 → IF7
It has been used as a solvent for handling metal fluorides. For example, the reduction of osmium hexafluoride with iodine is conducted in a solution in iodine pentafluoride:[7]
- 10 OsF6 + I2 → 10 OsF5 + 2 IF5
Primary amines react with iodine pentafluoride forming nitriles after hydrolysis[8]
Popular culture
Iodine pentafluoride is available as a "Special Gas" for flooding into the atmosphere of the escape shuttle in the terminal sequence of 1979 film Alien.
References
- Durbank, R. D.; Jones, G. R. (1974). "Crystal structure of Iodine Pentafluoride at -80°". Inorganic Chemistry. 13 (5): 421–439. doi:10.1021/ic50135a012.
- http://www.chemadvisor.com/Matheson/database/msds/mat11440000800003.PDF
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- Moissan, M. H. (1891). "Nouvelles Recherches sur le Fluor". Annales de Chimie et de Physique. 6 (24): 224–282.
- Ruff, O.; Keim, R. (1931). "Fluorierung von Verbindungen des Kohlenstoffs (Benzol und Tetrachlormethan mit Jod-5-fluorid, sowie Tetrachlormethan mit Fluor) [Fluoridation of Carbon Compounds (Benzene and Tetrachlormethane with Iodine-5-Fluoride, and Tetrachloromethane with Fluorine)]". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie (in German). 201 (1): 245–258. doi:10.1002/zaac.19312010122.
- Ruff, O.; Keim, R. (1930). "Das Jod-7-fluorid [The iodine-7-fluoride]". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie (in German). 193 (1): 176–186. doi:10.1002/zaac.19301930117.
- Holloway, John H.; Mitchell, S. J. (1971). "Preparation and Crystal Structure of Osmium Pentafluoride". Journal of the Chemical Society: 2789-94. doi:10.1039/J19710002789.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Stevens, T. E. (1966). "Rearrangement of Amides with Iodine Pentafluoride". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 31 (6): 2025–2026. doi:10.1021/jo01344a539.
Further reading
- Lord, R. C.; Lynch, M. A.; Schumb, W. C.; Slowinski, E. J. (1950). "The Vibrational Spectra and Structures of Iodine Pentafluoride and Heptafluoride". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 72 (1): 522–527. doi:10.1021/ja01157a135.
- Rogers, M. T.; Speirs, J. L.; Thompson, H. B.; Panish, M. B. (1954). "Iodine Pentafluoride, Freezing and Boiling Point, Heat of Vaporization and Vapor Pressure-Temperature Relations". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 76 (19): 4843–4844. doi:10.1021/ja01648a022.
- Rogers, M. T.; Thompson, H. B.; Speirs, J. L. (1954). "Dielectric Constants of Liquid Chlorine Trifluoride and Iodine Pentafluoride". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 76 (19): 4841–4843. doi:10.1021/ja01648a021.
- Booth, H. S.; Pinkston, J. T. Jr. (1947). "The Halogen Fluorides". Chemical Reviews. 41 (3): 421–439. doi:10.1021/cr60130a001.
- Hetherington, G.; Robinson, P.L. (1956). "The Viscosities of Iodine Pentafluoride and Ditellurium Decafluoride". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 3681. doi:10.1039/jr9560003674. ISSN 0368-1769.
External links
- WebBook page for IF5
- National Pollutant Inventory - fluoride and compounds fact sheet
- web elements listing