Nonane
Nonane is a linear alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C9H20. It is a colorless, flammable liquid, occurring primarily in the component of the petroleum distillate fraction commonly called kerosene, which is used as a heating, tractor, and jet fuel.[4] Nonane is also used as a solvent, distillation chaser, fuel additive, and a component in biodegradable detergents.[5]
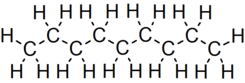 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Nonane[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
Beilstein Reference |
1696917 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.558 |
| EC Number |
|
Gmelin Reference |
240576 |
| MeSH | nonane |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1920 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C9H20 |
| Molar mass | 128.259 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Gasoline-like |
| Density | 0.718 g/mL |
| Melting point | −54.1 to −53.1 °C; −65.5 to −63.7 °F; 219.0 to 220.0 K |
| Boiling point | 150.4 to 151.0 °C; 302.6 to 303.7 °F; 423.5 to 424.1 K |
| log P | 5.293 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.59 kPa (at 25.0 °C) |
Henry's law constant (kH) |
1.7 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
Magnetic susceptibility (χ) |
-108.13·10−6 cm3/mol |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.405 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
284.34 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std molar entropy (S |
393.67 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−275.7–−273.7 kJ mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−6125.75–−6124.67 kJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H226, H304, H315, H319, H332, H336 |
GHS precautionary statements |
P261, P301+310, P305+351+338, P331 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
3
0
0 |
| Flash point | 31.0 °C (87.8 °F; 304.1 K) |
Autoignition temperature |
205.0 °C (401.0 °F; 478.1 K) |
| Explosive limits | 0.87–2.9% |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
none[2] |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 200 ppm (1050 mg/m3)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanes |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Nonane has 35 structural isomers.
Its substituent form is nonyl. Its cycloalkane counterpart is cyclononane, (C9H18).
Unlike most alkanes, the numeric prefix in its name is from Latin, not Greek. (A name using a Greek prefix would be enneane.)
Combustion reactions
Nonane undergoes combustion reactions that are similar to other alkanes. In the presence of sufficient oxygen, nonane burns to form water and carbon dioxide.
When insufficient oxygen is available for complete combustion, the burning products include carbon monoxide.
- 2C9H20 + 19O2 → 18CO + 20H2O
See also
- Higher alkanes
- List of isomers of nonane
References
- "nonane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0466". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- "NFPA Hazard Rating Information for Common Chemicals". Archived from the original on 2015-02-17. Retrieved 2015-03-13.
- "Petroleum - Chemistry Encyclopedia - reaction, water, uses, elements, examples, gas, number, name". www.chemistryexplained.com. Retrieved 2016-01-28.
- Health Council of the Netherlands: Committee on Updating of Occupational Exposure Limits. Nonane; Health-based Reassessment of Administrative Occupational Exposure Limits. The Hague: Health Council of the Netherlands, 2005; 2000/15OSH/155. http://www.gezondheidsraad.nl/sites/default/files/0015osh155.pdf Archived 2018-02-28 at the Wayback Machine
External links
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0466". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- MSDS at Oxford University
- List of isomers of nonane